Here Is The Below
Task
1:
Q1: Write a program to calculate the factorial of any given number by using recursion.
What Is Factorial
in
mathematics, the n!-denoted factorial
of a non-negative integer, is the sum of all positive integers that are less
than or equal to n. The factorial of n also equals the sum of the product of n
and the next smaller factorial:
Take, for instance, the value 0! is one, in accordance with the standard for an
empty product.
In other words, Say That the Factorial of a number
specifies a product of all integers from 1 to that number. It is defined by the
symbol exclamation mark (!).
For
example
: The factorial
of 5 is denoted as 6! = 1*2*3*4*5*6= 720.
Code:
def
recur_factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return n
else:
return n*recur_factorial(n-1)
num=int(input("Input
a number to compute the factorial : "))
# check
if the number is negative
if num
< 0:
print("Sorry, factorial does not exist
for negative numbers")
elif num
== 0:
print("The factorial of 0 is 1")
else:
print("The factorial of", num,
"is", recur_factorial(num))
Task 2:
Q2:Write an algorithm to calculate the
Fibonacci series of any given number using recursion.
Algorithm:
1. First
of all we will initialize the function of any name and pass argument=n.
2. Now
we will give the following if conditions to follow and find the Fibonacci series.
·
If n< 1 then return n.
·
If n> 1 call the function and
subtract 1 from the argument (n-1) and again call the function and subtract 2
from the argument.
3. And
in the last return and add these both functions.
What Is the Fibonacci
series?
A Fibonacci sequence is the integer sequence of 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8... The
first two terms are 0 and 1. All other terms are obtained by adding the
preceding two terms. This means to say the nth term is the sum of (n-1)th and (n-2) th term.
Task
3:
Write a program to Implement the Tower of Hanoi problem using
recursion.
What Is a Tower of Hanoi?
There are three rods and n disks in the Tower of
Hanoi, which is a mathematical puzzle. The puzzle requires you to follow the
straightforward guidelines below in order to transfer the entire stack to a
different rod.
1) You can only move one disk at a time.
2) Each move comprises of taking the upper circle
from one of the stacks and putting it on top of another stack for example a
plate must be moved in the event that it is the highest circle on a stack.
3) A larger disk cannot be stacked on top of a
smaller one.
Note: The transfer of the top n-1 disks from the
source rod to the auxiliary rod is a new problem that can be solved in the same
way.
Code:
def movedisk (fromPole, toPole):
print("Moving Disk from",fromPole,"to",toPole)
def moveTower (height,fromPole,toPole,withPole):
if height
>= 1:
moveTower(height-1,fromPole,withPole,toPole)
movedisk(fromPole,toPole)
moveTower(height-1,withPole,toPole,fromPole)
h =int(input("Enter Height:"))
fp=input("Enter point from pole:")
tp=input("Enter point to pole:")
wp=input("Enter point with pole:")
moveTower(h,fp,tp,wp)
Task 3:
Q3” Execute code 1 by appending your name, f_name,
cms_ID, and batch. Pop 1st two elements and attach the output.
What
Is Appending?
Since adding items to a list is a
common occurrence in Python, the language provides a plethora of methods and
operators to assist you. .append() is one of those approaches. You can add
items to the end of an existing list object using the.append() function. In a
for loop, you can also use.append() to programmatically populate lists.
Code:
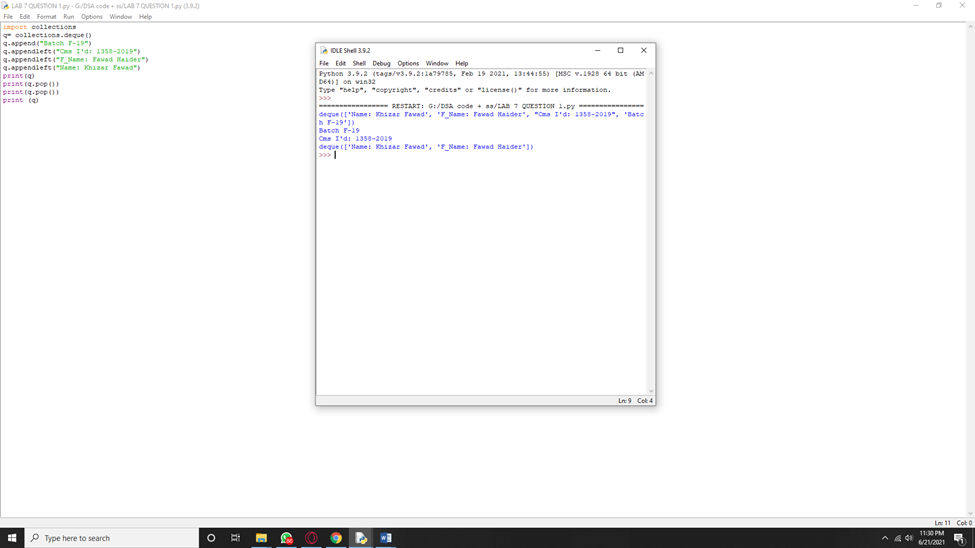
import collections
q= collections.deque()
q.append("Batch F-19")
q.appendleft("Cms I'd: 1358-2019")
q.appendleft("F_Name: Fawad Haider")
q.appendleft("Name: Khizar Fawad")
print(q)
print(q.pop())
print(q.pop())
print (q)
Task
4:
Complete code 2 by making the object
of the class queue and performing the following operations
·
Enqueue ( 3 times different data types)
·
Print q
·
Dequeue (2 times and print their
values)
What
Is Queue?
A queue is a linear data structure that operates in a First In, First Out (FIFO) order and is open at both ends.
Code:
class
Queue:
def
__init__(self):
self.items
= []
def
isEmpty(self):
return
self.items == []
def
enqueue(self, item):
self.items.insert(3,"item")
def
dequeue(self):
return
self.items.pop()
def
size(self):
return
len(self.items)
q=Queue()
q.enqueue(12)
q.enqueue('Khan')
q.enqueue(True)
print(q.size())
print(q.dequeue())
print(q.dequeue())
print(q.size())
Learning
Outcomes:
In
this lab, we learned about Recursion; the Fabbionacci Series & also Implementation
of Queues.













0 Comments